For those venturing into the world of poultry farming, understanding the art of candling chicken eggs in an incubator is crucial. Candling allows you to check the development of embryos inside the eggs, ensuring that your incubation process is on the right track. In this guide, well dive into the essentials of candling and how it contributes to successful hatching.
What is Egg Candling?
Egg candling is a method used to observe the growth and development of an embryo inside an egg. This technique involves shining a light source through the egg to see the contents inside. Its a practice that dates back centuries, originally using candles, which is how it got its name. Today, more efficient tools, such as LED lights, are used for better visibility.
The Importance of Candling
Candling is not just about seeing the inside of an egg; its a vital step in the incubation process. It helps in determining whether an egg is fertile or not, identifying any defects, and monitoring the embryo’s development. This practice ensures that only healthy embryos continue to incubation, improving hatch rates.
How to Candle Chicken Eggs
Learning how to candle chicken eggs effectively can make a significant difference in your hatching success. Heres a step-by-step guide:
Choose the Right Time
The best times to candle are on days 7, 14, and 18 of incubation. These days align with key stages in embryonic development, allowing you to make critical assessments.
Prepare Your Equipment
Ensure you have a proper light source. LED flashlights are highly recommended due to their brightness and ease of use. Make sure the room is dark to see the embryo clearly.
Handle with Care
When candling, gently pick up the egg and hold it to the light. Roll the egg slowly to observe all areas, but do so carefully to avoid damaging the embryo.
Interpreting What You See
While candling, youll see various features that indicate the eggs status:
Fertile Eggs
Fertile eggs will show a network of blood vessels and a dark spot, which is the developing embryo. As the days pass, the embryo will grow, making the egg appear darker.
Infertile Eggs
Infertile eggs remain clear, without any blood vessels. These should be removed to prevent them from affecting the other eggs.
Dead Embryos
If an embryo dies, the blood vessels will recede, and you might see a ring of blood. These eggs should also be removed promptly.
Benefits of Candling
Candling offers several benefits that contribute to the success of hatching eggs:
Monitoring Development
By observing the growth of the embryo, you can ensure it is developing correctly. This allows for timely interventions if there are issues.
Improving Hatch Rates
Removing infertile or non-viable eggs reduces the risk of contamination and helps maintain optimal incubation conditions for the remaining eggs.
Common Challenges in Candling
While candling is an invaluable tool, it comes with challenges such as:
Difficulty Seeing Through Dark-Shelled Eggs
Eggs with dark shells can be challenging to candle. In such cases, using a brighter light source or waiting until later in the incubation period may help.
Interpreting Results
Understanding what you see during candling can be confusing at first. With practice, however, you will become more adept at recognizing the signs of healthy or unhealthy embryos.
Conclusion
Candling is a critical skill for anyone involved in poultry farming. By mastering this technique, you can significantly enhance your success in hatching healthy chicks. Always remember to be gentle, observe regularly, and make informed decisions based on what you see.
Additional Resources
For more tips on raising healthy chickens, check out how to prepare herbs for chickens and how to clean a chicken coop naturally.
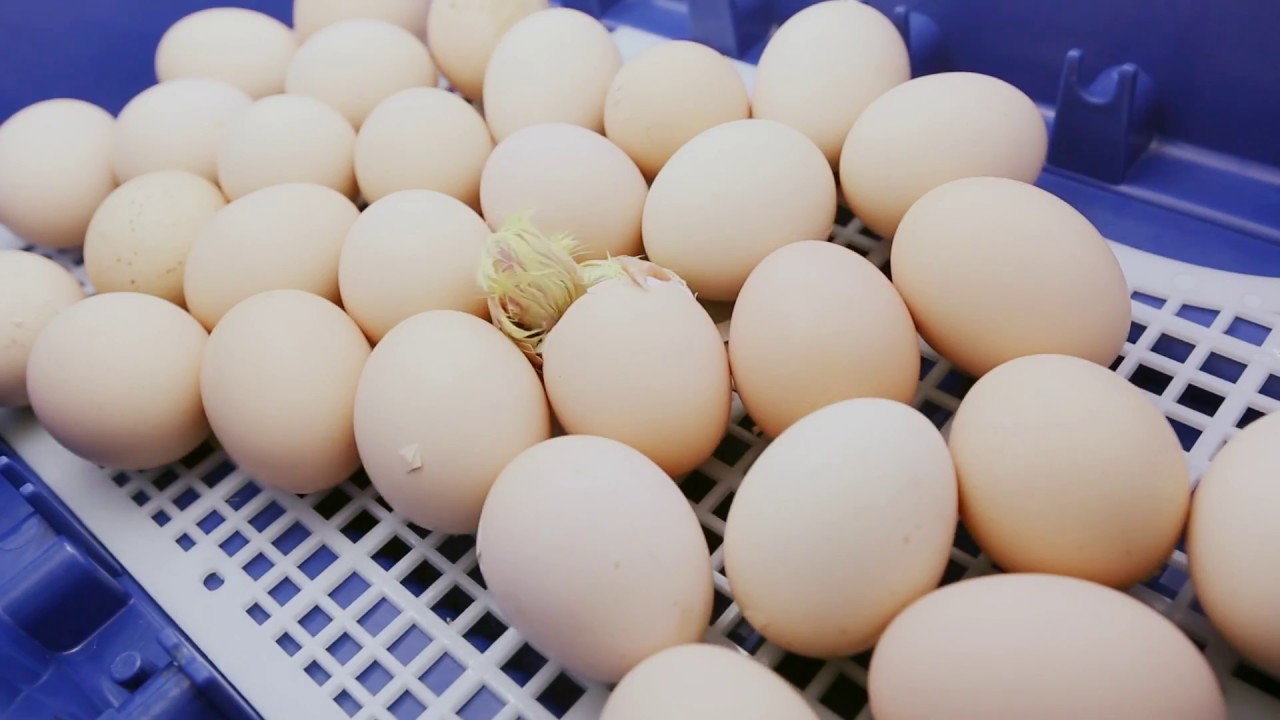

FAQs
What equipment do I need for candling?
A bright LED flashlight is recommended for candling. Ensure the room is dark to see the embryo clearly.
How often should I candle eggs?
Candle eggs on days 7, 14, and 18 of incubation to monitor development effectively.
Can I candle other types of eggs?
Yes, candling can be used for various types of bird eggs, including ducks and quails, following similar principles.
For more detailed information on egg incubation, visit this external guide on egg hatching.
This article contains affiliate links. We may earn a commission at no extra cost to you.